"Digital Logic Gates"
Digital Logic Gates
A Digital Logic Gate is a digital circuit which makes logical selections based at the mixture of virtual signals gift on its inputs.
A Digital Logic Gate is a digital circuit which makes logical selections based at the mixture of virtual signals gift on its inputs.
- Gate logic is also called as restoring logic. This is a logic circuitry designed so that even with an imperfect input pulse a standard output occurs at the exit of each successive logic gate.
- Digital logic gates can have more than one input, for example, inputs A, B, C, D, etc., but generally, only have one digital output. Individual logic gates can be connected or cascaded together to form a logic gate function with any desired number of inputs, or to form combinational and sequential type circuits, or to produce different logic gate functions from standard gates.
Digital Logic States
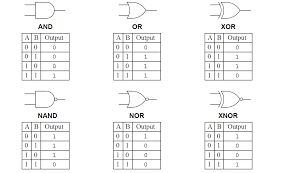
- The Digital Logic Gate is the basic building block from which all digital electronic circuits and microprocessor-based systems are constructed. Basic digital logic gates perform logical operations of AND, OR and NOT on binary numbers.In digital logic design, only two voltage levels or states are allowed and these states are generally referred to as Logic “1” and logic “0”, or HIGH and LOW, or TRUE and FALSE. These two states are represented in Boolean Algebra and standard truth tables by the binary digits of “1” and “0” respectively.A good example of a digital state is a simple light switch. The switch can be either “ON” or “OFF”, one state or the other, but not both at the same time.
Classification of Integrated Circuits
- Small Scale Integration or (SSI) – Contain up to 10 transistors or a few gates within a single package such as AND, OR, NOT gates.
- Medium Scale Integration or (MSI) – between 10 and 100 transistors or tens of gates within a single package and perform digital operations such as adders, decoders, counters, flip-flops, and multiplexers.
- Large Scale Integration or (LSI) – between 100 and 1,000 transistors or hundreds of gates and perform specific digital operations such as I/O chips, memory, arithmetic and logic units.
- Very-Large Scale Integration or (VLSI) – between 1,000 and 10,000 transistors or thousands of gates and perform computational operations such as processors, large memory arrays and programmable logic devices.
- Super-Large Scale Integration or (SLSI) – between 10,000 and 100,000 transistors within a single package and perform computational operations such as microprocessor chips, micro-controllers, basic PICs and calculators.
- Ultra-Large Scale Integration or (ULSI) – more than 1 million transistors – the big boys that are used in computers CPUs, GPUs, video processors, micro-controllers, FPGAs and complex PICs.
| Boolean Algebra | Boolean Logic | Voltage State |
| Logic “1” | TRUE (T) | HIGH (H) |
| Logic “0” | FALSE (F) | LOW (L) |



Comments