"Digital Logic Gates"
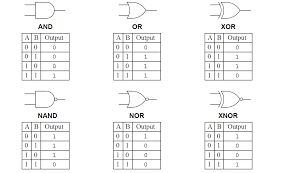
Digital Logic Gates A Digital Logic Gate is a digital circuit which makes logical selections based at the mixture of virtual signals gift on its inputs. Gate logic is also called as restoring logic. This is a logic circuitry designed so that even with an imperfect input pulse a standard output occurs at the exit of each successive logic gate. Digital logic gates can have more than one input, for example, inputs A, B, C, D, etc., but generally, only have one digital output. Individual logic gates can be connected or cascaded together to form a logic gate function with any desired number of inputs, or to form combinational and sequential type circuits, or to produce different logic gate functions from standard gates. Digital Logic States The Digital Logic Gate is the basic building block from which all digital electronic circuits and microprocessor-based systems are constructed. Basic digital logic gates perform logical operations of AND , OR ...



Comments